Webブラウザをユーザーインタフェースとして、サーバーサイドのプログラムを操作するために、最近はもっぱらTorando Web server を使っています。比較的リアルタイムにデータのやりとりを行うので、websocketで通信を行います。
ここで少し困ったのは、サーバーサイドで重い処理が行っている最中にブラウザから中断を指示したり、乱暴にブラウザをリロードしたときクイックにサーバサイドの処理を中断する方法がなかなかわかりませんでした。
一旦サーバサイドの処理が始まってしまうと、「websocketで中断指示を送信して、受信した側で中断フラグを立て、長時間処理のループのなかでフラグを参照して中断する」というやりかたがうまく行きません。ループ処理にブロックされて、websocketのサーバーサイドのメッセージ受信処理が先に進まないのです。
しばしお茶を飲んだり体をストレッチしたり首をコキコキしたりと無駄に時間を費やすうちに、ふと気が付きました。 処理を制御するためのwebsocketのストリームにいくらコマンドを送り付けてもブロックされてしまいますが、ブラウザのwebsocketの新しいストリームを立てるのは問題なくできます。そこで処理用のストリームのほかに、中断指示用のストリームをたてることにしました。さらに中断指示を受信したサーバー側のメッセージ処理のなかでは、中断フラグを立てるのではなく、キューに中断コマンドを書き込み、長時間処理のループのなかでキューからコマンドを取り出し、中断指示であればループをブレークするようにします。
こんな感じの対処で首尾よくタイトルの課題を解決できました。よくありそうなケースなので備忘としてサンプルコード化したロジックを掲載しておきます。ソースコードのなかで利用されてモジュール類は事前にインストールしておきます。
1.サーバーサイドのメイン処理プログラム
処理のメインプログラムです。以下のコードをlongrun.pyとして保存します。
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import tornado.websocket
import tornado.gen
import json
from sqlalchemy.orm import scoped_session
from models import SessionLocal, User, Task
import asyncio
interrupt_queue = asyncio.Queue() # 中断コマンドを格納するキュー
class ProcessingWebSocket(tornado.websocket.WebSocketHandler):
"""
タスク処理用のWebSocketハンドラ
"""
def initialize(self):
self.interrupted = False # 中断フラグ
self.db_session = scoped_session(SessionLocal) # データベースセッション
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def open(self):
print("タスク処理WebSocketが開かれました")
yield self.write_message("タスク処理WebSocket接続が確立されました")
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def on_message(self, message):
print(f"受信メッセージ: {message}")
self.interrupted = False # 中断フラグを初期化
# クライアントからのメッセージをJSONとして解析
data = json.loads(message)
username = data.get("username")
task_name = data.get("task")
if not username or not task_name:
yield self.write_message("無効なメッセージ: ユーザー名とタスクが必要です")
return
# データベースからユーザーを取得または作成
user = self.db_session.query(User).filter(User.username == username).first()
if not user:
user = User(username=username)
self.db_session.add(user)
self.db_session.commit()
# データベースからタスクを取得または作成
task = self.db_session.query(Task).filter(Task.user_id == user.id, Task.task_name == task_name).first()
if not task:
task = Task(user_id=user.id, task_name=task_name)
self.db_session.add(task)
self.db_session.commit()
try:
# タスク開始メッセージを送信
yield self.write_message(f"タスク '{task_name}' をユーザー '{username}' のために開始します...")
result = yield self.long_running_task(task)
# タスク完了メッセージを送信
if not self.interrupted:
task.is_completed = True
self.db_session.commit()
yield self.write_message(f"タスク '{task_name}' が完了しました: {result}")
else:
yield self.write_message(f"タスク '{task_name}' は中断されました。")
except tornado.websocket.WebSocketClosedError:
print("タスク処理中に WebSocket が閉じられました。")
except Exception as e:
print(f"タスク処理中のエラー: {e}")
finally:
self.db_session.close()
# 長時間実行タスク
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def long_running_task(self, task):
for i in range(50): # 長時間実行タスクをシミュレート
try:
# キューから中断フラグをチェック
interrupt_flag = interrupt_queue.get_nowait()
if interrupt_flag:
self.interrupted = True
return "中断されました"
except asyncio.QueueEmpty:
pass
task.progress = (i + 1) * 10
self.db_session.commit()
yield self.process_step(i + 1, task.task_name)
return f"タスク処理完了: {task.task_name}"
# 各ステップの処理
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def process_step(self, step, task_name):
try:
# 各ステップの進行状況を送信
yield self.write_message(f"タスク '{task_name}' のステップ {step}/50 を処理中")
yield tornado.gen.sleep(1)
except tornado.websocket.WebSocketClosedError:
print("ステップ処理中に WebSocket が閉じられました。")
raise
# WebSocket接続が閉じられたときに呼ばれる
def on_close(self):
print("タスク処理 WebSocket が閉じられました")
self.interrupted = True # 中断フラグをセット
def check_origin(self, origin):
return True # クロスオリジンを許可(開発用)
class InterruptWebSocket(tornado.websocket.WebSocketHandler):
"""
中断コマンドを処理するWebSocketハンドラ
"""
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def open(self):
print("中断WebSocketが開かれました")
yield self.write_message("中断WebSocket接続が確立されました")
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def on_message(self, message):
if message == "interrupt":
yield interrupt_queue.put(True) # 中断コマンドをキューに追加
yield self.write_message("中断コマンドが受信されました")
else:
yield self.write_message("不明なコマンド")
def on_close(self):
print("中断WebSocketが閉じられました")
def check_origin(self, origin):
return True # クロスオリジンを許可(開発用)
class LongRunHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
"""
クライアントサイドHTMLを表示するハンドラ
"""
def get(self):
self.render("templates\\longrun.html")
# Tornadoアプリケーションを作成する関数
def make_app():
return tornado.web.Application([
(r"/websocket_processing", ProcessingWebSocket),
(r"/websocket_interrupt", InterruptWebSocket),
(r"/longrun", LongRunHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = make_app()
app.listen(8888) # ポート8888でサーバーを起動
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()2. データベースとテーブルの定義
データベースはPostgreSQLかSQLiteです。SQLAlchemyを使って必要なテーブル類をクラス(ユーザ定義用とタスク管理用)として利用できるようにします。以下のコードをmodels.pyとしてメインプログラムと同じディレクトリに保存します。以下の例ではデータベース名はlongrundbとしました。
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String, Boolean, ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship
# データベースの定義
Base = declarative_base()
#DATABASE_URL = "postgresql+psycopg2://username:password@localhost/longrundb"
DATABASE_URL = 'sqlite:///longrundb.sqlite'
engine = create_engine(DATABASE_URL)
# User と Task のテーブル定義
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'users'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
username = Column(String, unique=True, nullable=False)
tasks = relationship("Task", back_populates="user")
class Task(Base):
__tablename__ = 'tasks'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
task_name = Column(String, nullable=False)
progress = Column(Integer, default=0)
is_completed = Column(Boolean, default=False)
user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('users.id'))
user = relationship("User", back_populates="tasks")
# SQLAlchemy のセッションを用意する
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
3. クライアントサイドのHTML/Javascript
マルチユーザでの動作を想定しているので、ユーザ名をサーバーに送信できるようにしています。タスクの開始用、タスク中断用にそれぞれwebsocketのストリームを割りあてます。以下のコードをtemplates\longrun.htmlとして保存します。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>WebSocket タスク処理</title>
<style>
#log {
width: 100%;
height: 300px; /* 固定の高さ */
border: 1px solid #ccc;
overflow-y: auto; /* 縦方向のスクロールを有効にする */
padding: 10px;
margin-top: 20px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>WebSocket タスク処理</h1>
<!-- ユーザー名を入力するフィールド -->
<input type="text" id="username" placeholder="ユーザー名を入力してください">
<button onclick="startTask()">タスク開始</button>
<button onclick="sendInterrupt()">タスク中断</button>
<div id="log"></pre>
<script>
let processingSocket; // タスク処理用のWebSocket
let interruptSocket; // タスク中断用のWebSocket
// ログを表示する関数
function log(message) {
const messageDiv = document.getElementById("log");
// メッセージを追加
messageDiv.innerHTML += `<p>${message}</p>`;
// 新しいメッセージが追加された後、常に一番下にスクロール
messageDiv.scrollTop = messageDiv.scrollHeight;
}
// タスク処理用WebSocketを開く関数
function openProcessingWebSocket() {
processingSocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8888/websocket_processing");
processingSocket.onopen = function() {
log("タスク処理WebSocket接続が開かれました");
};
processingSocket.onmessage = function(event) {
log("サーバーからのメッセージ: " + event.data);
};
processingSocket.onclose = function() {
log("タスク処理WebSocket接続が閉じられました");
};
}
// 中断用WebSocketを開く関数
function openInterruptWebSocket() {
interruptSocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8888/websocket_interrupt");
interruptSocket.onopen = function() {
log("中断WebSocket接続が開かれました");
};
interruptSocket.onmessage = function(event) {
log("サーバーからのメッセージ: " + event.data);
};
interruptSocket.onclose = function() {
log("中断WebSocket接続が閉じられました");
};
}
// タスク開始時に呼び出される関数
function startTask() {
const username = document.getElementById("username").value;
if (!username) {
log("ユーザー名を入力してください");
return;
}
openProcessingWebSocket();
processingSocket.onopen = function() {
log("ユーザー " + username + " のタスクを開始します");
const taskMessage = JSON.stringify({ username: username, task: "SampleTask" });
processingSocket.send(taskMessage); // ユーザー名とタスクを送信
};
}
// 中断コマンドを送信する関数
function sendInterrupt() {
if (!interruptSocket || interruptSocket.readyState !== WebSocket.OPEN) {
openInterruptWebSocket();
}
interruptSocket.onopen = function() {
log("中断コマンドを送信します");
interruptSocket.send("interrupt");
};
}
// ウィンドウが閉じられたときにWebSocket接続を閉じる
window.onbeforeunload = function() {
if (processingSocket) {
processingSocket.close();
}
if (interruptSocket) {
interruptSocket.close();
}
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. プログラムを実行する
作成したコードの配置は以下のようになっています。
longrun.py
models.py
templates\
-- longrun.htmlメインプログラムを実行します。
>python longrun.pyブラウザを起動してURLとして次を入力します。 localhost:8888/longrun
マルチユーザに対応しているので、上記のURLを二つのブラウザの画面で開いてみます。画面イメージは以下のようになります。それぞれに異なるユーザ名を入力します。タスク開始ボタンをクリック後、タスク中断ボタンをクリックすると、処理が中断されます。また、処理の途中でブラウザをリロードすると、サーバサイドの処理が中断されます。
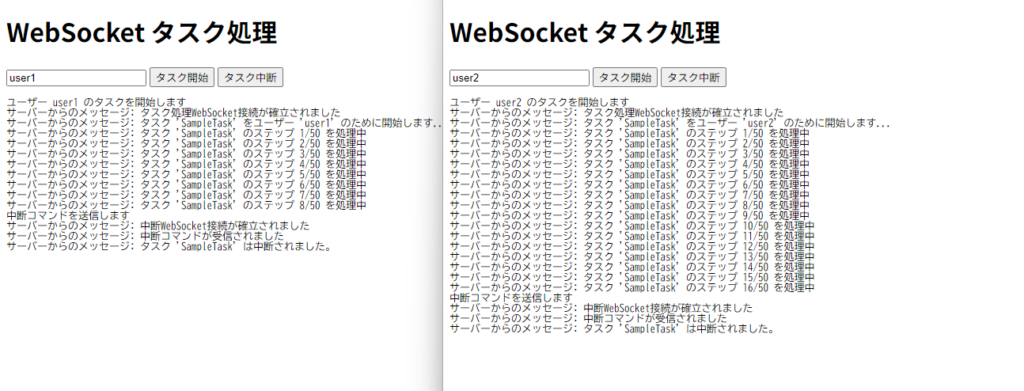
以上です。